Rare Semi-Aquatic Beetle Found in Eastern Ghats
Species spotted in Tirupati 100 years after Sri Lanka
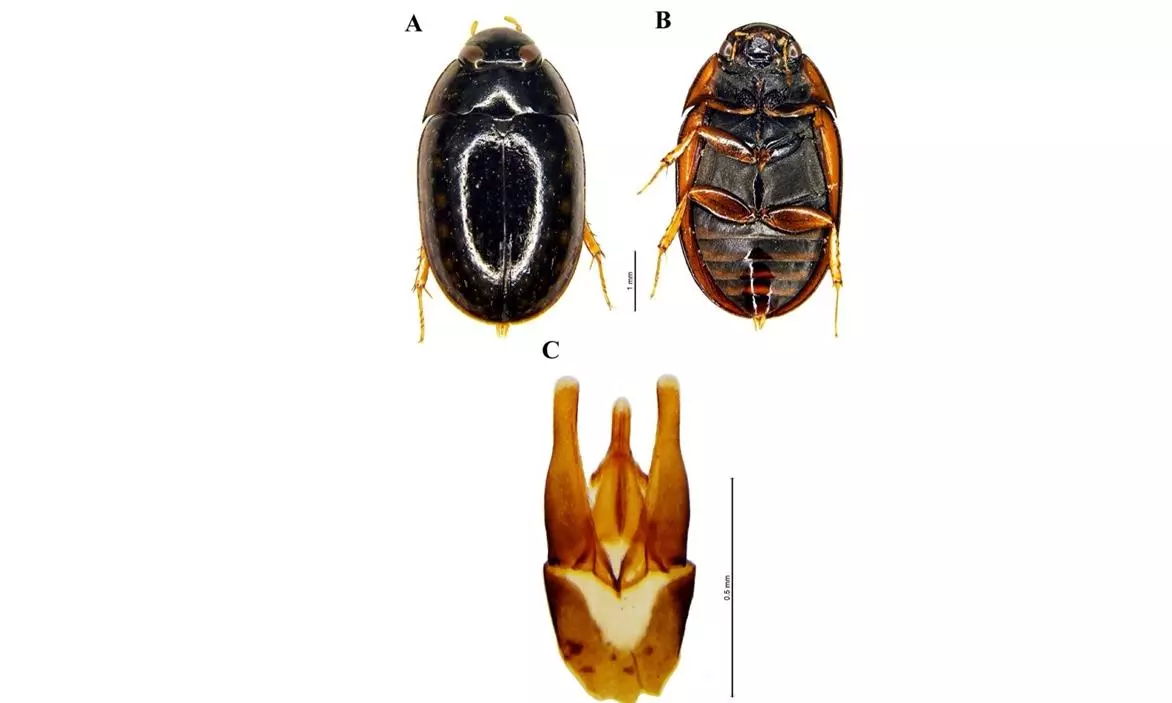
Visakhapatnam: Scientists of the Zoological Survey of India have documented the presence of a rare semi-aquatic beetle species in India.
This signifies an expansion of its known geographic distribution, found more than 100 years after it was originally sighted in Sri Lanka.
The ZSI said the species originally identified from Madulsima, Sri Lanka, is known as S. Spinosa. It was found in the Eastern Ghats near Kalyani Dam, Tirupati, within the Seshachalam biosphere reserve.
The collaborative research effort involved scientists from the ZSI’s freshwater biology regional centre in Hyderabad and the Virudhunagar Hindu Nadars Senthikumara Nadar College in Tamil Nadu.
For species identification, researchers employed traditional morphological analysis and modern molecular techniques. “The team used DNA barcoding of the cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (COI) gene along with phylogenetic analysis using Maximum Likelihood methods and the K2P model,” explained Deepa Jaiswal, officer-in-charge of ZSI's freshwater biology regional centre.
The beetle was discovered in hygropetric habitats, specialized environments characterised by slow water seepages on rocky surfaces. In these microhabitats, S Spinosa was found coexisting with other aquatic beetle species.
The study was led by Shiva Shankar from the freshwater biology regional centre of the ZSI in Hyderabad, alongside colleagues Devadoss Kumar, Deepa Jaiswal, Karuthapandi Madasamy and Shrikant Jadhav.

