Hyderabad: Installing unverified root certificates can lead to fraud
The certificates are issued by the Root Certifying Authority of India (RCAI), which is not verified by Google.
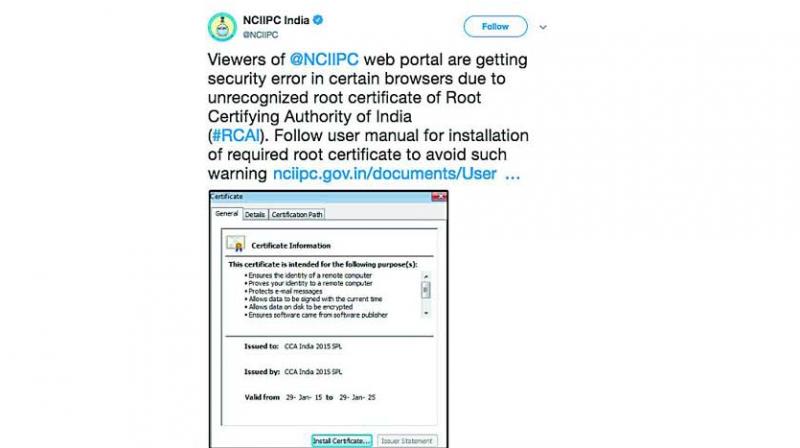
Hyderabad: The next time you visit a website, do not ignore the security errors, even if it is a government website. Always check the URL to see if the connection is secure. In a hurry to navigate to a website, users often tend to accept terms or click the ‘ignore’ button on the warning that pops up when visiting a site.
People often see a security error reported especially by certain web browsers like Google Chrome for sites which begin with http://. Such was the case with National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC) which in April asked users to instal a root certificate.
For secure communication to happen over internet (https:// in the URL), root certificates are used to avoid unscrupulous users from targeting you. The certificates are issued by the Root Certifying Authority of India (RCAI), which is not verified by Google.
Installing unverified root certificate amounts to fraud and impersonation. Experts suggest avoiding installation of the certificate if any website asks you to do so, as they can commit fraud on you.
Mr Kiran Jonnalagadda of Internet Freedom Foundation said, “The direction that NCIIPC gave basically means anyone who issues a root certificate can pretend to be any website in the world. If you install the certificate, like that from the NCIIPI, they can pretend to be google.com and your browser won’t warn you that it is an incorrect website. They can commit fraud on you”. Websites like NCIIPI get the certification from RCAI. Google doesn’t recognise RCAI as a trusted entity because it has been misused in the past.
Mr Ranjit Raj of Swecha FSMI said, “The certificate issued by RCAI is not credible. Many certificates are issued without any scrutiny. There was a conversation between Google and RCAI but it was left hanging without a proper redressal mechanism. Even the NCIIPI certificates were updated.”
The previous version of browsers like Internet Explorer, Firefox and Google were not firm about secure connections. But they are more keen about security (https://) now as modern browsers don’t allow a http:// connection without issuing warning.
Mr Jonnalagadda said that the certificate issue happens because of poor organisational controls. “Root certifying authority certificates were misused in the past which is why Google doesn’t trust them any more. Some sites pretend to be Google and the Chrome browser has recognised it. Chrome no longer recognises or issues certificate because it amounts to fraud. A organisation has to be extremely thorough with its processes, if not it will be a vector for fraud,” he added.

