Google Turns Quadratic Equations Into Mathematical Fun
Google's Doodle illustrates how the equation can be applied to real-life scenarios across various fields, including physics, engineering, sports, and business.
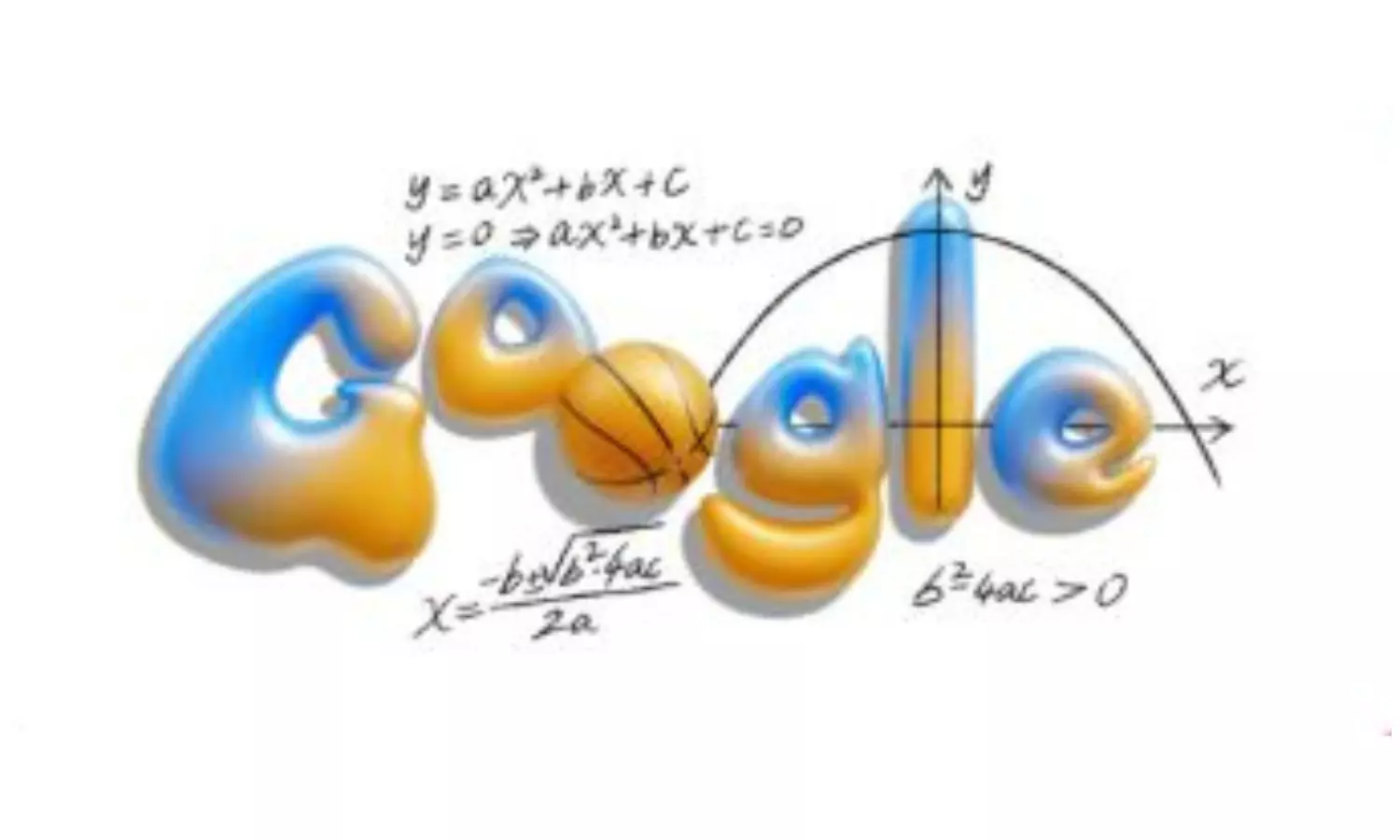
Google's homepage features a basketball-themed parabola, celebrating the quadratic equation.
While the Google Doodle marked the start of the US and UK academic year in September, it has now rolled out in other countries, including India. Clicking on the doodle leads users to Google's Gemini AI, which takes a moment to explain the application of the quadratic equation to a game of basketball.
What is the quadratic equation?
Although the equation can seem like another confusing algebraic formula, it is used to calculate real-world motion, including the arc of a basketball shot.
Today's Google logo depicts a fun, playful bubble font with an orange-blue gradient, with one of the 'o's acting as a basketball that moves in the curve of a parabola. The general form and solution of the equation surround it.
Revising the formula
y = ax² + bx + c
This is the quadratic function whose graph forms a parabola.
a, b, c are constants, where a ≠ 0
x is the variable.
y = 0
To find the value of x (roots or zeroes), set y = 0
So, ax² + bx + c = 0
b² - 4ac
This is the discriminant, which tells you the nature of the roots and how many real solutions the quadratic has.
If b² - 4ac > o, then there are two real, distinct roots and the parabola crosses the x-axis twice, thus creating the curve of a basketball shot.
x = (-b±√(b²-4ac))/(2a)
This is the quadratic formula to find the solutions.
Google's Doodle illustrates how the equation can be applied to real-life scenarios across various fields, including physics, engineering, sports, and business.
After clicking on the doodle, users can insert numerical values for speed, time, and height to see how the ball's path changes with different variables.
With this interactive doodle, Google reminds us that learning is not limited to the classroom. Connecting textbook equations to real-life examples can help students understand concepts better and retain information more efficiently.
Ancient Roots
The quadratic equation first appeared in ancient Babylon around 2000 BCE, where they used geometric methods to solve quadratic problems. Similar techniques were also used in Ancient Greece and Egypt to measure lengths and areas.
However, the first systematic method to solve quadratic equations dates back to 628 CE in India. Mathematicians like Brahmagupta created the first general solution to such problems.
The article has been written by Tejasree Kallakrinda, an intern at Deccan Chronicle

